Procurement teams must effectively balance business priorities by collaborating with internal teams to tackle external challenges and turn them into opportunities. The stronger the partnership between procurement and other internal functions, the greater the likelihood of achieving compliance, saving costs, and meeting enterprise objectives.
Managing suppliers, sourcing, contracting, and spending is essential for enterprise success. Difficulties in procuring raw materials can significantly impact the entire value chain. These challenges were particularly pronounced during major events such as the US-China trade war, the COVID-19 pandemic, and the recent geopolitical conflicts. Enterprises experience external challenges that are out of their scope of control; however, many internal challenges (such as the group’s alignment, compliance, and cost savings) can be managed. For a value-driven procurement, creating synergy between the functions and leadership is essential.
HFS Research promotes the OneEcosystem framework, where enterprise employees, customers, and partners collaborate to generate new sources of value. Procurement teams focus on driving costs down and collaborate internally to reduce blind spots and save costs. They must consider internal and external factors to be efficient, cost-conscious, compliant, and sustainable (see Exhibit 1).
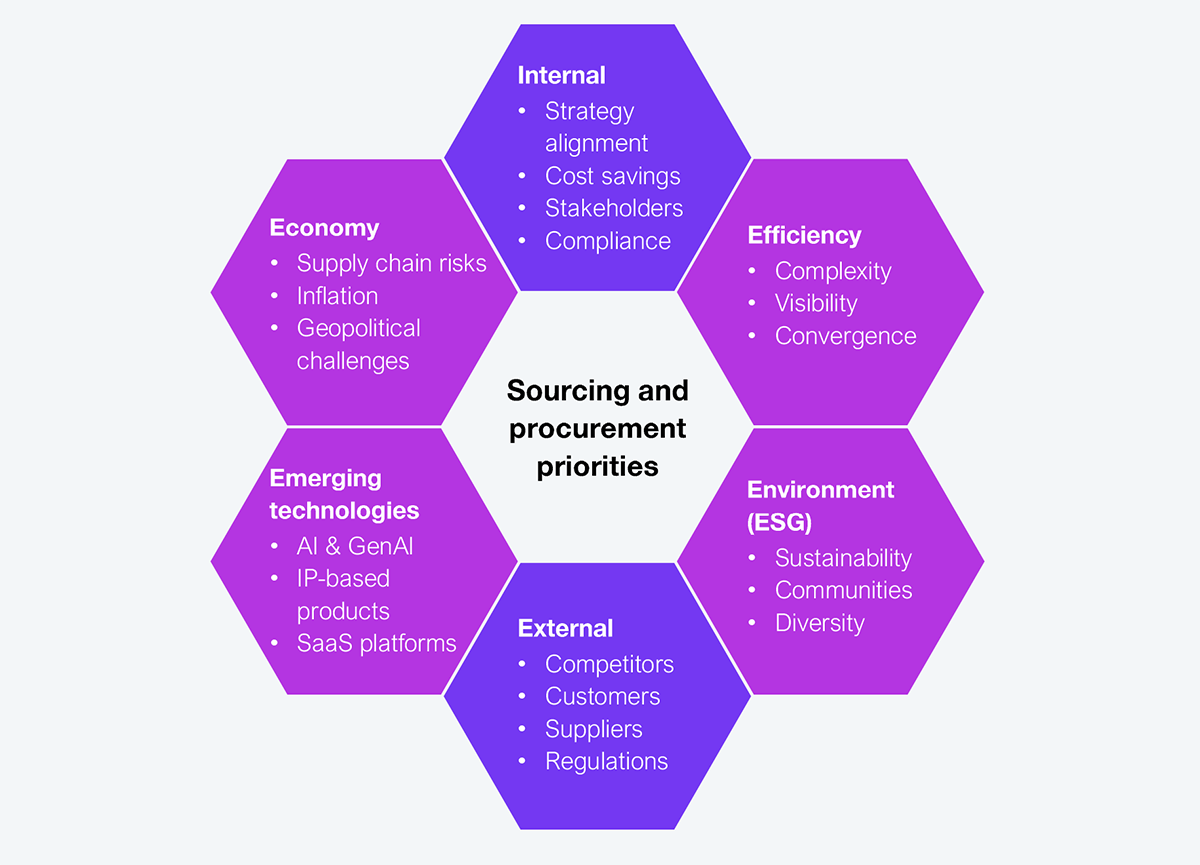
Source: HFS Research, 2024
Procurement leaders should evaluate different scenarios, including the effects of high inflation, the energy index, and the consumer price index (CPI) on their organization. They must also assess how the energy index can influence product pricing and affect negotiation terms with suppliers. Price changes driven by these indicators can vary depending on the industry in which the enterprise operates. Working with internal teams is essential for making the most of these scenarios when relevant. For instance, a European retail company operates stores across Europe and collaborates with multiple suppliers to source various fast-moving consumer goods. A slight change in the pricing makes a big difference to company margins due to the high volume of each product procured for its extensive store network. The suppliers regularly adjust and increase prices based on the consumer price index (CPI) every quarter, regardless of whether the CPI directly impacts the product. Most suppliers took advantage of these indices during the geopolitical tensions in Europe and charged their customers even after normalcy.
The retail company’s leadership initiated internal cooperation among the data science, pricing, sourcing, and procurement teams, realizing that the suppliers took advantage of the indicators by overcharging. They aimed to identify high-volume procured product costs through the value chain, including raw material prices, labor, and energy expenses. The teams created a model that provides a list of products affected by the CPI or the energy price index, facilitating discussions or negotiations on these cost factors. The IT teams performed scenario-based analyses of the products, which triggered many interactions with the suppliers. They commenced discussions with the suppliers, yielding significant benefits for the retail company, reducing the product pricing where there is no impact of the CPI or the energy index, and increasing collaboration internally and with the suppliers.
The procurement function is an enterprise ecosystem builder due to its magnitude of impact throughout the organization. For instance, a banking company wants to upgrade to cloud and other software-as-a-service (SaaS) platforms. Several teams are involved in selecting the right cloud and SaaS platform while ensuring the bank meets its technical, regulatory, and business needs. The central procurement team works closely with internal stakeholders, including legal, compliance, and finance, to gather requirements, issue RFPs, and evaluate bids. This team coordinates the entire process, ensuring compliance with vendor management policies, negotiating terms, and securing the best possible pricing. They collaborate with IT and security teams to assess the technical aspects of the platform, including compatibility with existing systems, scalability, and cybersecurity measures. The security team ensures the platform complies with regulatory standards, such as the Federal Financial Institutions Examination Council’s (FFIEC) guidelines for safeguarding sensitive financial data.
The procurement process at the bank involves procurement leaders, senior management, and stakeholders from various departments, including operations, finance, and risk management. Together, they make decisions to ensure that the selected platform aligns with the bank’s broader digital transformation strategy and business objectives. This collaborative approach helps address operational efficiency and regulatory compliance. Failure to collaborate can incur significant penalties. For example, Deutsche Bank and its US affiliates were fined $186 million by the Federal Reserve in 2023 for neglecting to address money laundering control issues. The bank was also instructed to enhance its risk and data management.
Procurement leaders can be proactive by devising strategies and scenarios that leverage the minds of cross-functional teams and by using cutting-edge technologies to achieve their corporate objectives, address potential challenges, and ensure smooth operations.
Register now for immediate access of HFS' research, data and forward looking trends.
Get StartedIf you don't have an account, Register here |
Register now for immediate access of HFS' research, data and forward looking trends.
Get Started